Top Nodejs Features Explained
In today’s fast-paced digital world, developers need tools that are not only efficient but also scalable and performance-driven. Node.js stands out as a powerful JavaScript runtime environment that has revolutionized backend development. But what exactly makes it so special? The secret lies in its rich set of features.
From its event-driven architecture to non-blocking I/O and real-time capabilities, Node.js offers developers a modern and efficient approach to building web applications. Whether you’re developing APIs, microservices, or full-stack apps, understanding the core features of Node.js is essential for leveraging its full potential. In this article, we’ll explore the key Node.js features that make it a top choice for modern web development.
Asynchronous and Event-Driven Nodejs Features
One of the standout Node.js features is its asynchronous, event-driven architecture. This allows the server to handle multiple requests simultaneously without blocking the execution thread.
Real-Time Application Support as a Nodejs Feature
Another powerful Node.js feature is its built-in support for real-time applications, such as chat apps or live dashboards. Thanks to libraries like Socket.io, Node.js makes it easy to implement two-way communication between the server and client.
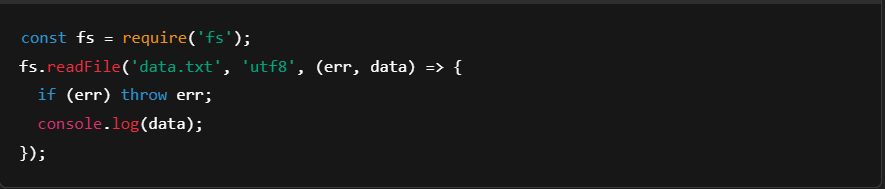
1. Asynchronous and Non-blocking I/O
Node.js operates asynchronously, allowing multiple operations to run in parallel without blocking the main thread. This improves performance and responsiveness.
Example:
Why It Matters:
Efficient handling of multiple connections without creating new threads saves resources and enhances scalability.
2. Single-threaded Event Loop Model
Node.js uses a single-threaded model with event looping, which enables handling many connections simultaneously.
Example:
Why It Matters:
This model is highly efficient for I/O-heavy operations, like APIs or real-time applications.
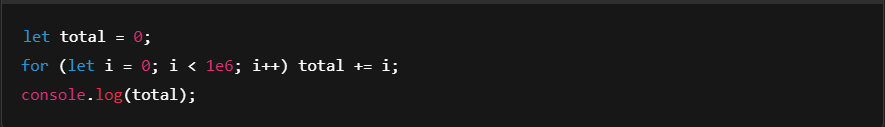
3. Fast Execution with V8 Engine
Node.js uses the Google Chrome V8 engine, which compiles JavaScript to native machine code for lightning-fast performance.
Example:
Why It Matters:
Fast execution makes Node.js ideal for performance-critical applications.
4. Built-in Package Manager (npm)
Node.js comes with npm, the world’s largest ecosystem of open-source libraries and modules.
Example:
Why It Matters:
Developers can integrate third-party libraries quickly, accelerating development cycles.
5. Cross-platform Development
Node.js supports multiple platforms (Windows, Linux, macOS), enabling cross-platform development with tools like Electron or NW.js.
Example:
Create desktop apps using:
Why It Matters:
Build once, deploy anywhere — from web to desktop.
6. Real-time Data Handling
Node.js is perfect for real-time applications like chat apps and gaming servers.
Example:
Why It Matters:
It supports WebSockets and event-driven communication for real-time updates.
7. JSON Support for APIs
Node.js natively handles JSON, simplifying data interchange between frontend and backend.
Example:
Why It Matters:
Streamlines building RESTful APIs and microservices.
8. Scalability and Microservices Architecture
Node.js is modular and lightweight, making it a great fit for microservices and scaling horizontally.
Example:
Use clustering for scale:
Why It Matters:
Improves performance and isolates services for easier maintenance.
9. Rich Ecosystem of Libraries
The Node.js ecosystem offers thousands of libraries for every purpose—from testing to deployment.
Example:
Popular packages:
Express.js (web framework)
Mongoose (MongoDB ODM)
Jest (testing)
Why It Matters:
These libraries reduce boilerplate code and speed up development.
10. Active Community and LTS Support
Node.js has a large, active developer community and offers long-term support (LTS) versions.
Example:
Latest LTS version:
Why It Matters:
Continual updates, tutorials, and community support ensure longevity and reliability.
10 Practical Use Cases of NodeJS Features
Chat applications – Real-time messaging using WebSockets
REST APIs – Fast, scalable APIs with Express
Real-time dashboards – Live updates using event-driven architecture
IoT apps – Handle data streams from multiple sensors
Microservices – Isolated services using Node clusters
Streaming services – Efficient I/O handling for video/audio
Desktop apps – Electron-based cross-platform apps
eCommerce backends – Fast product listing and checkout processes
Social media apps – Handle high user concurrency
DevOps tools – Build CLIs and automation scripts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What makes Node.js faster than other backend technologies?
- Node.js compiles JavaScript into machine code using the V8 engine, and its non-blocking architecture handles many operations simultaneously.
2. Is Node.js good for enterprise applications?
- Yes, many enterprises like Netflix and Walmart use Node.js for scalable, real-time applications due to its performance and microservices architecture.
3. Can Node.js be used with databases?
- Absolutely. Node.js supports databases like MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Redis through npm packages.
4. What are the limitations of Node.js?
- Node.js is single-threaded and may not be suitable for CPU-intensive tasks, but workarounds like clustering and worker threads exist.
5. How does Node.js compare to Python?
- Node.js is better for real-time and event-driven apps, while Python is preferred for data science and CPU-heavy tasks.
Conclusion
Node.js continues to revolutionize backend development with its robust features. From asynchronous I/O to a rich npm ecosystem, the nodejs features discussed here empower developers to build fast, scalable, and modern web applications.
Whether you’re building APIs, real-time systems, or cross-platform apps, Node.js provides the flexibility and performance to meet your needs.